About AptaDB
Aptamers are single-stranded nucleic acids, including DNA and RNA, that are capable of folding into various secondary structures and forming unique three-dimensional structures upon recognition and binding to specific target molecules. Because of their high selectivity and affinity for target molecules and their ability to interact with many types of targets, aptamers are used in a variety of applications such as biosensors, target recognition, and target delivery.
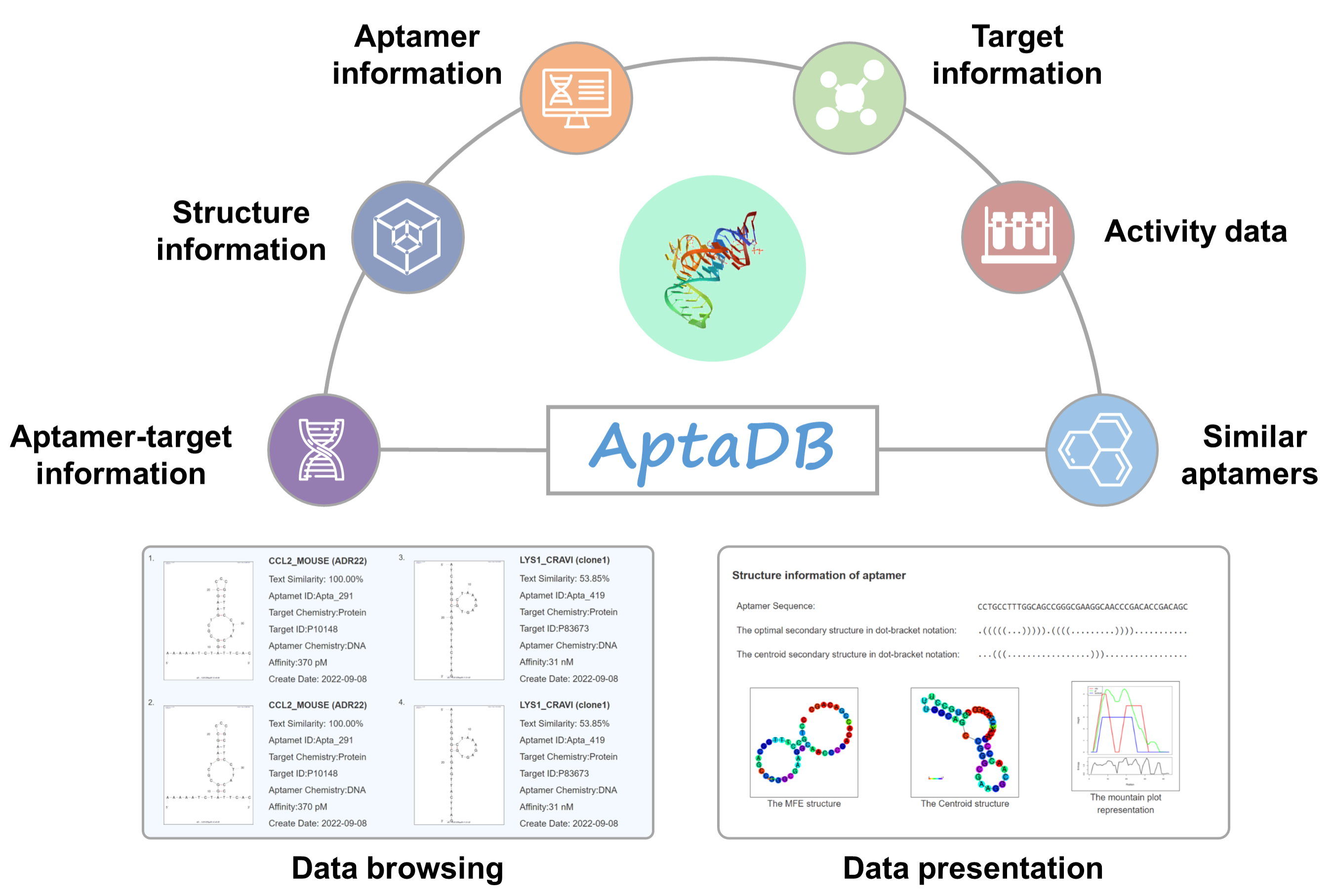
Here, we provide a public and comprehensive database named the AptaDB. The sequences, biological activity data, and physicochemical properties of these aptamers were manually extracted from the scientific literature or calculated by programs, and the related target information, mainly including proteins, small molecules, cells, introduced from other databases, respectively. The detailed information page of AptaDB presents the above information in six sections: aptamer-target interaction information, aptamer structure information, aptamer information, target information, activity data, and similar aptamers. The number of tetrads and G-Score were predicted by QGRS Mapper software as a complement to the aptamer structure information. In addition, the RDkit package (version 2022.03.1) predicts LogP, TPSA, hydrogen bond acceptors, hydrogen bond donors, etc. for small molecules. Using the Levenshtein distance algorithm, similarity between aptamers was calculated. On the Help page,you can learn more about the different modules. New data will be added and the user interface will be improved. Please contact us if you have any feedback, suggestions, bugs, or error reports.
What can AptaDB do?
- Search for binding aptamers based on target molecules, relevant literature
- Initially obtain possible binding aptamers based on similarity search
- Identify structural information of aptamer and target, basic properties
- Initially obtain aptamer screening conditions from experimental information
- Obtaining valuable interaction data as a resource for detecting potential aptamer-target interactions
- Utilizing AptaDB data to explore aptamer structure and pocket information



